Heart Stent Laser Processing
High-precision laser processing behind the industrialization of heart stents
Data shows that, on average, one Chinese patient uses a coronary stent every half a minute. On November 5, 2020, the country opened the purchase of high-value medical consumables. The original average price of 13,000 yuan of heart stents was reduced to less than 700 yuan. This frightening process only took 15 minutes, but the story behind it Much more complicated.
Behind the big jump in the price of heart stents is the joint support of the medical industry and policies. There is also a more important point: laser processing is more and more applied to the medical industry with its unique advantages to solve problems that cannot be overcome by traditional processing. Facilitate the technological innovation and upgrading of industrialized heart stent processing.
Heart stent: laser technology continues the life of patients
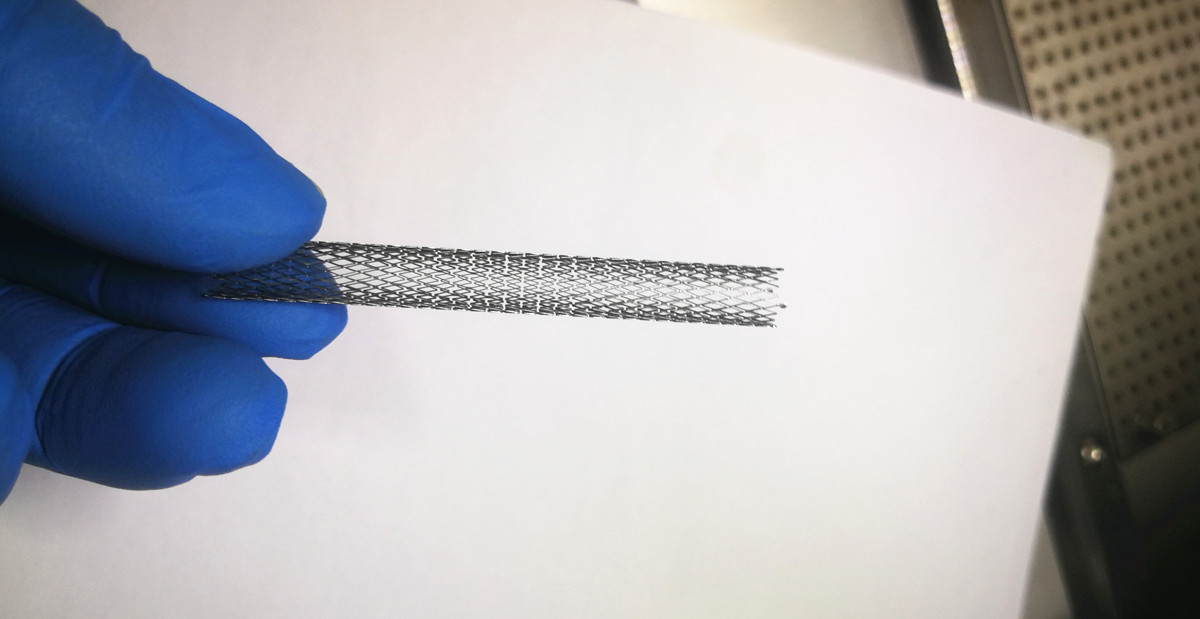
Heart stents first appeared in the 1980s and are also called coronary stents. They are equipment used for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and are one of the three main methods for the treatment of coronary heart disease. The diameter of the heart stent is only 2-4 mm, and the weight is less than one ten thousandth of a gram. It is a more direct and effective tool to deal with acute myocardial infarction. It can follow the blood vessel to the position where the coronary artery is blocked, and quickly open the blocked blood vessel, thereby restoring and maintaining the normal circulation of blood for a long time.
Since the heart stent is directly implanted in the human body, in-depth study must be carried out on the characteristics and safety of use, and extremely demanding conditions must be met. For example, requirements for flexibility, anti-thrombosis, biocompatibility, and support. The wall tube of the heart stent is extremely thin, and it needs to be manufactured using a precision laser cutting process. The use of ordinary laser processing will cause the heart stent to have many burrs, and the width of the cut groove is not uniform. The heart stent made in this way cannot meet the conditions of use.
In recent years, foreign companies have begun to use femtosecond lasers for stent cutting. Femtosecond laser refers to a laser whose time-domain pulse width is on the order of femtoseconds (femtoseconds, 10^-15 seconds). The strong electric field generated by the short pulse of femtosecond laser eliminates the free electrons near the tangent point of the material, so that the positively charged materials are repelled by the same sex, and the force between the molecules is lost. The material removal is completed by “molecule removal”. The heart stent processed in this way has no burrs, a smooth surface, no thermal damage, no ablation, high cutting accuracy, and uniform rib width.
Metal cardiovascular stent implantation is currently the most used method for the treatment of vascular diseases. In 2014, Clare and others of the NCLA/Inspire Laboratory of the National University of Ireland used femtosecond lasers with a pulse width of 500 fs, a frequency of 100 kHz, and a wavelength of 1030 nm and 515 nm to induce two periodic surfaces on the surface of stainless steel. Structure, and studied the effects of two periodic structures on fibroblasts and monocytes. The results show that the microstructure surface is not conducive to the adhesion of blood cells, thereby reducing the chance of coagulation, improving the blood compatibility of the vascular stent, and increasing the cycle and depth will reduce the adhesion of cells.
Since the metal stent will remain permanently in the artery after implantation, there is a risk of medical complications. In order to reduce this risk, the concept of absorbable stents has also become a research hotspot today. The stent can be made of materials such as poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) and polylactic acid (PLA), but this material has a low melting point and is sensitive to thermal effects, which greatly increases the difficulty of the processing process.
Ultrafast laser is used to process and manufacture the absorbable stent, so that the thermal effect of the laser beam energy on the stent material is minimized. However, the current absorbable vascular stents manufactured by ultrafast laser micro-nano are expensive and low in yield. How to use this technology to realize the industrialization of vascular stents is an urgent problem for researchers.
Technical iteration of laser precision machining
Laser-processed heart stents were first used in foreign countries, mainly in Europe, the United States, and Japan. For a long time, due to the lack of mature technical conditions, the quality of the finished stents manufactured is not high enough, so the domestic stent market is basically occupied by foreign companies.
In recent years, with the in-depth research and development of domestic research institutions and the rise of laser companies, many technical difficulties have begun to be overcome. Subsequently, the R&D and production of cardiac stent suppliers began to adopt laser precision processing technology.
In 2014, Cheng Ping and others of Hefei University of Technology used femtosecond laser processing technology, supplemented by the chair-shaped design of the processing bush, and successfully prepared a degradable heart stent sample. The sample holder structure has no thermal damage, the cutting edge is smooth and the rib width consistency is about ±6μm.
In 2017, the Xi’an Institute of Optics and Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences combined its traditional superior disciplines and took femtosecond laser precision intelligent manufacturing as the key breakthrough direction of the institute. It successfully developed an industrialized cardiac stent femtosecond laser high-precision processing equipment, which solved the low processing accuracy of domestic cardiac stents. , Inconsistent rib width, many burrs and other processing defects, realized high-precision and low-damage cutting processing of a variety of materials, improved the performance and service life of domestic heart stents, and reached the international first-class quality level. This equipment solves the “bottleneck” technical problem that restricts the laser cutting of cardiac vascular stents, improves the technical level and core competitiveness of my country over the laser industry and the medical device industry, and promotes the rapid development of the entire cardiac stent industry in my country.
Heart stents can be divided into second-generation metal stents and third-generation biodegradable stents according to their materials. Laser processing is the best processing method due to factors such as small size, thin structure, and high requirements for appearance and mechanical properties.
Ordinary fiber lasers can complete the processing of most metal stents, while bioabsorbable stents are made of degradable polymer materials, which are easily thermally degraded during melt processing, low light absorption, and easy carbonization in processing. “Hot” processing is difficult to undertake this task. Femtosecond lasers with ultra-high peak power and ultra-short pulses have significant advantages. By adjusting the process parameters, it can achieve the “cold” processing effect of smooth cutting edges of degradable materials without carbonization, which perfectly solves the above problems.
To this end, Han’s Laser Source Division has launched a femtosecond laser cutting equipment for medical stents, which provides the best solution for processing the third generation of biodegradable stents. The use of a specific jig structure can solve the processing problems caused by insufficient mechanical strength of the degradable stent pipe, and ensure the relative position, the stability of the focal spot size and the consistency of the stent rib width during processing. The equipment is used for precision cutting of stent products in the medical device industry. It mainly cuts degradable materials such as polylactic acid (PLA) and poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), and is compatible with 316 stainless steel, nickel-titanium alloy, cobalt-chromium alloy, magnesium-aluminum alloy and other metals Precision cutting of materials.
The continuous improvement of the strength of “China Laser Manufacturing” not only brings direct benefits to the general public, but also gives us the confidence and confidence to break the monopoly of foreign technology. It can be said that from the domestic replacement of heart stents, a momentum of independent research and development has swept the entire manufacturing industry. The next five years will be five years in which China’s manufacturing industry will explode from the low-end to the high-end, and the ultimate beneficiaries will be local Chinese consumers.
About Cheersonic
Cheersonic is the leading developer and manufacturer of ultrasonic coating systems for applying precise, thin film coatings to protect, strengthen or smooth surfaces on parts and components for the microelectronics/electronics, alternative energy, medical and industrial markets, including specialized glass applications in construction and automotive.
Our coating solutions are environmentally-friendly, efficient and highly reliable, and enable dramatic reductions in overspray, savings in raw material, water and energy usage and provide improved process repeatability, transfer efficiency, high uniformity and reduced emissions.
Chinese Website: Cheersonic Provides Professional Coating Solutions

