Differentiating Features of PTCA Balloons
Differentiating Features of PTCA Balloons – Ultrasonic Spraying PTCA – Cheersonic
Angioplasty balloon catheters can differ in size, material used, in their construction and the compliance the balloon has to the lumen of the vessel. Depending on lesion extension and density, PTCA balloons require specific features, such as lesion-crossing capability, vector force or pressure to push plaque out of the way or break up calcium.
The PTCA balloon catheter market is segmented by its level of compliance in conforming to the shape of the vessel lumen. These subdivisions include compliant, non-compliant and semi-compliant balloons. Semi-compliant PTCA balloons are used in pre-dilatation of the lesion before the stent implantation. The non-compliant balloon catheters are usually ultra-high strength to handle the overinflation pressures to break up calcified lesions and to expend stents. Compliant balloons are low pressure and conform to the lumen size.
Balloon catheters also can be segmented on the basis of balloon material used, which includes the use of polyurethane, nylon materials, and polyethylene (PE), polyolefin copolymer (POC) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyolefins are used as balloon material for their good tensile strength and compressibility that allows the balloon to rapidly inflate and deflate during the procedure. Polyethylene is a light, versatile, thermoplastic polymer. Polyethylene terephthalate is a type of polyester that is used for the production of high-pressure balloons.
Nylon holds the largest share in the balloon catheter market. This is mainly owing to the benefits of nylon because it is softer, it is more easily refolded and is easier to withdraw into the guiding catheter or introducer sheath. When compared with PET versions, nylon high-pressure balloons require a thicker wall for a given burst pressure, which means that a nylon balloon will have a larger profile than a comparable PET balloon upon insertion into the body and when crossing a lesion. Polyethylene is growing in usage because of its ability to inflated by volume, rather than pressure. These balloons are able to stretch 100% to 800% and are often used in applications that require the balloon to fully conform to, or occlude, the anatomy.
Polyurethane is considered the most desirable material used for the manufacturing of balloon catheters due to its tensile strength, hemocompatibility and biocompatibility.
Other materials such as terephthalate and silicone, which have a suitable co-efficient of friction, pressure ratings and radial force that minimizes vessel injury during insertion, may also contribute to the market.
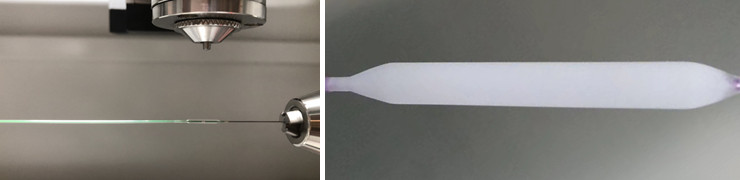
Ultrasonic Spraying PTCA Balloons
Ultrasonic Balloon Catheter Coating System is suited to coating high pressure medical balloons with drug eluting polymers such as Paclitaxel and other bioabsorbable drugs for dilation procedures including coronary angioplasty or stent delivery applications.
The Balloon Catheter Coating System is a fully enclosed, sealed glovebox unit designed to coat common sizes and types of balloon catheters using Cheersonic ultrasonic nozzles combined with our UAM7000 precision air shaping systems. The spray pattern diameter and drop size are variable, depending upon the nozzle and air shaping system used. A proprietary holding device secures both ends of the catheter while rotational motors spin the catheter for 360Ocoverage of the entire balloon surface. The ultrasonic nozzle traverses across the catheter as required to coat desired lengths. The system includes controls for air flow rate, air pressure as well as continuous digital metering of humidity and temperature.
Paclitaxel Coated PTA Peripheral Balloon Catheter

